The Surprising Benefits of Intermittent Fasting: A 2025 Guide

The Surprising Benefits of Intermittent Fasting: A 2025 Guide explores various methods, health improvements, and crucial safety considerations for individuals considering this dietary approach in the coming year, providing a comprehensive overview of its potential benefits and necessary precautions.
Is The Surprising Benefits of Intermittent Fasting: A 2025 Guide right for you? This article delves into the science-backed benefits, practical tips, and potential risks of this popular dietary approach, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health journey in the year ahead.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting: A Primer for 2025
Intermittent fasting (IF) has surged in popularity, with many people exploring its potential to improve health and well-being. But what exactly is intermittent fasting, and why is it gaining so much traction as we approach 2025?
In essence, intermittent fasting is not about *what* you eat, but rather *when* you eat. It’s an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and voluntary fasting on a regular schedule.
Different Types of Intermittent Fasting
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to intermittent fasting. Several different methods can be tailored to your individual needs and lifestyle.
- 16/8 Method: This involves fasting for 16 hours each day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. For example, you might eat between 12 pm and 8 pm and fast for the remaining 16 hours.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: This method involves fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week. For instance, you might eat dinner on Monday and then not eat again until dinner on Tuesday.
- 5:2 Diet: With this approach, you eat normally for five days of the week and restrict your calorie intake to 500-600 calories on the other two non-consecutive days.
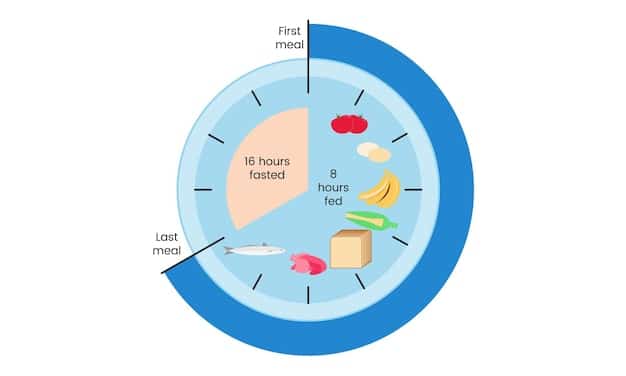
The popularity of intermittent fasting stems from its flexibility and its potential benefits beyond just weight loss. Many find it easier to adhere to than traditional calorie-restrictive diets because it doesn’t require constant monitoring of food intake, but rather a focus on timing.
The Science-Backed Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
As we move closer to 2025, robust scientific research continues to support the potential benefits of intermittent fasting. While more studies are always needed, current evidence suggests that IF can impact several key areas of health.
Let’s examine some of the most promising findings:
Weight Management
Intermittent fasting can be an effective tool for weight management. By restricting the eating window, individuals often naturally consume fewer calories. Furthermore, IF can boost metabolism by increasing levels of norepinephrine (noradrenaline), a hormone that promotes fat burning.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Improved insulin sensitivity reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Brain Health
Emerging research suggests that intermittent fasting may benefit brain health. IF can increase the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that promotes the growth and survival of brain cells. This could potentially protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Cellular Repair: Intermittent fasting triggers a process called autophagy, where cells remove waste and repair themselves.
- Heart Health: IF may improve various heart health markers, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and triglycerides.
- Longevity: Some animal studies suggest that intermittent fasting can extend lifespan. While more research is needed in humans, the potential for longevity benefits is intriguing.
It’s important to note that the results of intermittent fasting can vary from person to person. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and the specific fasting protocol can all influence outcomes.
Choosing the Right Intermittent Fasting Method for You
Deciding to embark on an intermittent fasting journey requires careful consideration of your individual needs and health status. Not all intermittent fasting methods are created equal, and what works for one person may not work for another.
Here’s a guide to help you choose the most suitable approach:
Consider Your Lifestyle
Think about your daily routine and identify potential challenges. If you have a demanding job that requires consistent energy levels, a less restrictive method like the 16/8 may be more suitable than a 24-hour fast. Ensure the chosen method aligns with your social life and commitments.
Assess Your Health Status
Before starting any intermittent fasting regimen, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or a history of eating disorders. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid intermittent fasting.
Start Gradually
Don’t jump into the deep end. Begin with a less intense method, such as the 16/8, and gradually increase the fasting duration as your body adapts. This approach minimizes potential side effects like hunger, fatigue, and irritability.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how you feel during fasting periods. If you experience significant discomfort or adverse effects, adjust your fasting schedule or consider a different method.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, especially during fasting periods, to maintain hydration and prevent headaches.
- Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: When you are eating, prioritize whole, unprocessed foods that provide essential nutrients. This helps to ensure you get all the vitamins and minerals you need.
Ultimately, the best intermittent fasting method is the one that you can consistently adhere to and that aligns with your health goals and lifestyle.
Foods to Eat (and Avoid) During Your Eating Windows
Intermittent fasting focuses primarily on *when* you eat, but the *what* you eat during your eating windows is still vitally important. Fueling your body with the right foods can maximize the benefits of IF and support your overall health goals.
A balanced and nutrient-rich diet is key to success.
Foods to Emphasize
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods that provide essential nutrients and support satiety:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Load up on a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, which are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Lean Protein: Choose lean sources of protein like chicken, fish, beans, and lentils to support muscle mass and keep you feeling full.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, which are essential for hormone production and brain function.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Minimizing processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can enhance the effectiveness of intermittent fasting and improve your overall health:
- Processed Foods: Limit your intake of processed foods like packaged snacks, fast food, and sugary cereals, which are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and added sugars.
- Sugary Drinks: Avoid sugary drinks like sodas, juices, and sweetened beverages, which can spike blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain.
- Unhealthy Fats: Minimize your consumption of unhealthy fats from sources like fried foods, processed meats, and refined oils, which can increase your risk of heart disease.

Planning your meals ahead of time can help you stay on track and make healthier choices during your eating windows. Consider meal prepping on the weekends to ensure you have nutritious options readily available throughout the week.
Potential Risks and How to Mitigate Them
While intermittent fasting offers numerous potential benefits, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks and side effects. Understanding these risks and taking steps to mitigate them can help ensure a safe and successful IF experience as you approach 2025.
Individual responses to IF can vary greatly, so it is important to pay attention to how your body reacts.
Common Side Effects
Some people may experience side effects such as:
- Hunger and Cravings: This is often the most common side effect, especially during the initial stages of IF. Manage hunger by drinking plenty of water, consuming fiber-rich foods during eating windows, and staying busy.
- Headaches: Dehydration and changes in blood sugar levels can trigger headaches. Ensure adequate hydration and consider adding electrolytes to your water.
- Fatigue and Irritability: These can occur due to reduced calorie intake and fluctuations in blood sugar. Adjust your fasting schedule and prioritize adequate sleep.
Who Should Avoid Intermittent Fasting?
Certain individuals should avoid intermittent fasting altogether or consult with their healthcare provider before starting:
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: IF can deprive the developing fetus or infant of essential nutrients.
- Individuals with Eating Disorders: IF can exacerbate eating disorder tendencies.
- Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes: IF can lead to dangerous fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetics should consult with their doctor.
Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new dietary regimen, including intermittent fasting, to determine if it’s right for you and to address any potential health concerns.
Intermittent Fasting in 2025: What the Future Holds
As we look ahead to 2025, intermittent fasting is poised to become even more integrated into mainstream health and wellness practices. Ongoing research is continuously uncovering new insights into its long-term effects and potential applications.
Here’s what we can anticipate in the coming years:
Personalized Approaches
As our understanding of genetics and individual responses to IF grows, we can expect to see more personalized approaches tailored to specific needs and preferences. This may involve genetic testing to determine the optimal fasting protocol and dietary recommendations for each individual.
Technological Advancements
Technology will play an increasingly important role in supporting IF practices. Wearable devices and apps can track fasting periods, monitor calorie intake, and provide personalized feedback, helping individuals stay on track and achieve their goals.
Integration with Other Health Practices
Intermittent fasting is likely to be combined with other health practices, such as exercise, mindfulness, and stress management techniques, to create a holistic approach to well-being.
While the future of intermittent fasting appears promising, it’s important to approach it with a critical and informed perspective. Stay tuned for ongoing research and consult with your healthcare provider to determine if IF is right for you.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ⏱️ Timing Matters | IF focuses on *when* you eat, cycling between eating and fasting periods. |
| 🍎 Food Quality | Nutrient-dense foods during eating windows enhance IF benefits. |
| ⚠️ Potential Risks | Be aware of hunger, headaches, and other side effects; consult a doctor if needed. |
| 🚀 Future Trends | Expect personalized IF approaches and integration with technology. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The 16/8 method is extremely popular due to its flexibility and ease of integration into daily life. It involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window, often fitting well with typical schedules.
Yes, IF can be effective for weight loss. By restricting eating windows, it often leads to reduced calorie intake. Additionally, it may boost metabolism and promote fat burning, contributing to weight reduction.
No, IF is not safe for everyone. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with a history of eating disorders, and those with type 1 diabetes should avoid IF. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential before starting.
Focus on nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These options provide essential nutrients and support satiety, maximizing the benefits of intermittent fasting for overall health.
Consistency is key, and noticeable results can often be seen within a few weeks to a couple of months. It’s important to listen to your body and adjust your approach for long-term sustainability and health benefits.
Conclusion
As we journey into 2025, the surprising benefits of intermittent fasting are capturing widespread attention. Remember that while IF shows promise, it’s crucial to approach it thoughtfully, considering your individual health needs and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals. Whether you’re aiming for weight management, improved health markers, or simply a more structured eating pattern, intermittent fasting offers a flexible and potentially rewarding approach when implemented responsibly.